As AI agents became more advanced, Google has developed an innovative Agent2Agent (A2A) protocol to simplify their interaction and make it possible for them to work together on the same task within a certain ecosystem. This solution enabled the company to streamline the functioning of multi-agent systems (MAS) and make connections between AI-powered bots less complicated while enhancing their protection. A2A is fully transparent and utilizes HTTP, JSON-RPC, and SSE frameworks to facilitate auditing and ensure compliance. In this guide, we will analyze how A2A creates a unified ruleset and streamlines coordination between all kinds of AI solutions across various domains.
What is the Agent2Agent Protocol?
The A2A is a widely adopted standard developed to optimize interaction and cooperation between AI tools, making it possible to handle complex requests. Google introduced it to expedite data exchange between modern frameworks and vendors and simplify access to schema-based JSON data. Besides, A2A facilitates handling HTTP POST requests, dealing with Task IDs, transferring message objects, and learning more about the core capacities of a certain tool within the environment. It allows virtual assistants to entrust each other with responsibilities and team up to bring projects to completion.
A2A fixes the widespread issue found in many MAS. It facilitates negotiating interaction modalities and makes complex frameworks flexible and effective.
Function calling allowed custom-built LLMs designed for the needs of enterprises from across various industries to establish connections via APIs. However, as each vendor used a unique approach to integration, it was challenging to achieve proper interoperability.
The main objective of the model context protocol (MCP) was to offer a procedure to address the NxM challenge, where N stands for independent algorithm-based tools and systems, and M refers to the number of features and sources they should integrate with. MCP does not support direct AI agent communication. As LLMs became complicated, engineers started to rely on A2A, which empowered them to improve the functionality of their digital products.
A2A offers a standard way for AI boots to join forces. It is innovative and allows them to access data about the specific capabilities of others and collaborate with them on projects that require a complex approach. Besides, it helps developers build more complex projects in various languages without programming when working on each integration.
Main Benefits of A2A
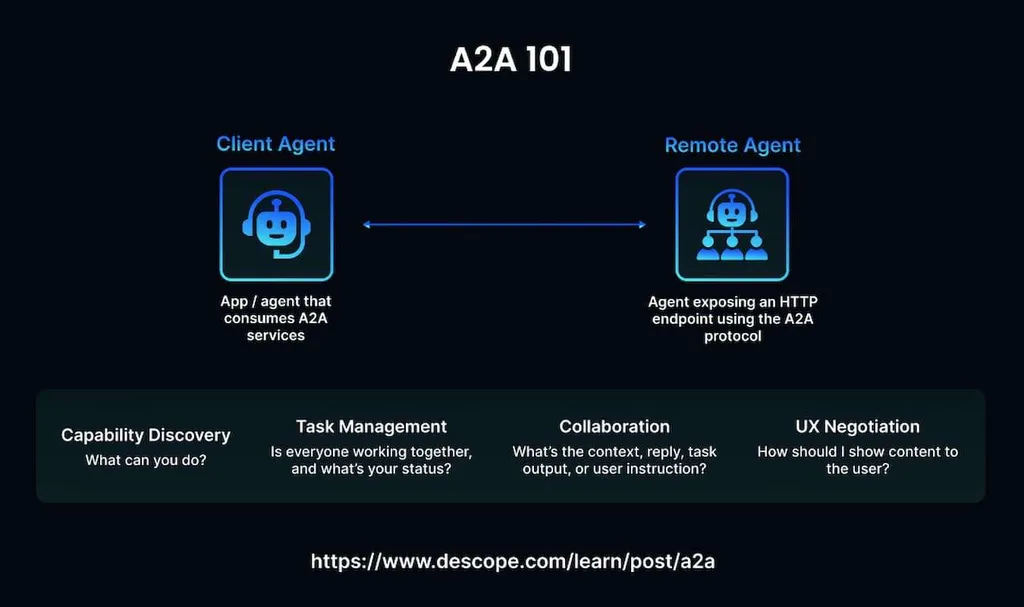
The standard supports several essential functionalities. They simplify collaboration between networked services. An endpoint functions as the main actor that specifies which problems should be resolved and distributes them. Agent2Agent servers operate as remote agents (RAs) responsible for determining specific requests. The most critical features of the standard are the following:
- Capability discovery. Agent cards stored as JSON files enable the main node to discover the most suitable RA for dealing with an issue. Such profiles facilitate understanding what services each AI solution specializes in.
- Task management. Clients and RAs coordinate approaches to solve an issue. They synchronize their efforts when working on time-consuming tasks.
- Collaboration. Assistants exchange messages to understand the context and instructions and create a seamless conversation flow.
- User experience negotiation. AI assistants can decide how to present content to a user. They negotiate the right format and analyze key UI capabilities, including iframes and video. In addition, they change the way they present data based on the ability of an RA to handle it.
These capacities make A2A the most efficient modern standard, which explains its popularity among developers.
Key A2A Components
A2A has quickly become the main standard adopted by complex environments. Its effectiveness relies on several important elements:
- Agent Card. In most situations, it’s hosted at a typical web address. In the JSON file, one can request the description of a specific tool’s features, learn about authentication guidelines, and discover the endpoint URL. The file contains comprehensive information. Such data can be read by other machines. After analyzing it, assistants can decide whether they can benefit from using such services.
- A2A Server. This RA can detect HTTP endpoints based on the Agent2Agent protocol. It receives requests and solves tasks. Information about its capabilities can be found on cards.
- A2A Client. Such systems create tasks and decide which servers have the right capacities to solve them. They excel in workflow orchestration.
- Task. Each issue has a unique ID and a current status that shows various degrees of its completion (submitted, finalized). Tasks function like containers for the issues a system is requested to solve or the features that should be implemented.
- Message. They are used in communication between the client and the tool. They are exchanged when a particular task should be solved. Each message includes Parts with certain content. It could be TextPart for text, File Part for binary information, or DataPart for forms and other types of JSON data.
At first, Google described its agents using the term opaque, referring to their ability to collaborate on requests without disclosing the internal logic. Agents need to explain only what problems they can solve, but they do not have to reveal the methods and algorithms they use. It allows MAS to remain highly secure.
How Does A2A Function?
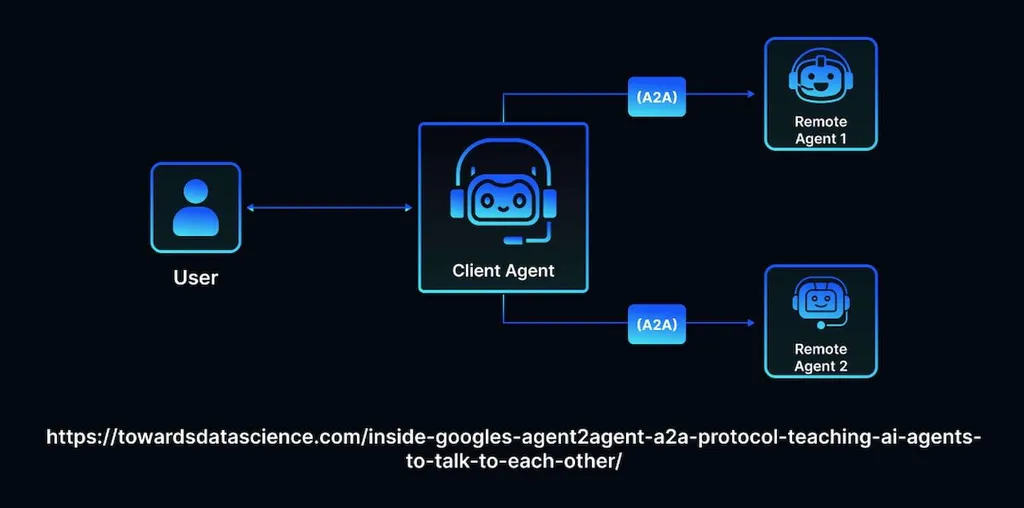
It facilitates two-way communication between AI tools functioning across diverse environments. When a user initiates a task, the client sends a request to the server’s endpoint and assigns a unique ID. It is accompanied by a message that provides detailed information about the request. Then, the removed agents start looking for specific information that matches the criteria set by a user. They may complete the task quickly if relevant data is available and easy to access, or ask a user to clarify their request.
The protocol allows agents to perform such tasks:
- Discover information about each other’s functionalities. When a user submits a request to the central agent and asks it to perform a certain task, like planning a trip, the AI bot they are chatting with understands that they need to access information about hotels and tourist attractions that can be retrieved and provided by other tools.
- Send structured messages and provide data about the context with the help of message objects and special data fields.
- Work together on projects while following strict security and privacy policies.
- Bringing convoluted tasks to completion and getting timely updates and notifications on the progress status.
The usage of MCP and A2A allows companies to benefit from a broader agentic architecture, enabling AI assistants to handle convoluted tasks by coordinating efforts and using advanced reasoning capabilities.
Security remains one of the upsides to implementing the protocol, as it guarantees that agents will be able to communicate without disclosing valuable insights to unauthorized parties. Each AI component may fully trust the identity of another unit. The protocol relies on API keys and advanced authentication schemes. It enables it to verify and confirm the identity of assistants and prevent leakage.
The standard utilizes dynamic UX negotiation practices and permits tools to adjust their performance depending on interactions. It helps them remain efficient in all sorts of environments and adjust their practices depending on the current scenario.
Due to the implementation of the A2A protocol, companies manage agents and processes across multiple platforms and environments. It lets them integrate AI tools with their systems with ease, augment security, and implement innovative approaches.
Real-World Applications of A2A
Nowadays, enterprises seek to deploy AI solutions to handle routine tasks automatically and allow employees to focus on high-priority cases. Agent2Agent was quickly adopted across companies and organizations interested in deploying powerful AI systems. Here are the main use cases of the standard:
- Enhancing customer experience. AI agents use data provided by chatbots, deploy transaction processors, and utilize recommendation engines. It allows them to provide high-quality support services and access information from multiple sources to generate replies relevant to user queries. Due to their high effectiveness, such solutions increase consumer satisfaction.
- Simplifying supply chain operations. Dedicated AI tools optimize inventory management, predict changes in demand depending on seasonal trends and other data, and make logistics operations more efficient.
- Healthcare and diagnostics. Several AI agents work with each other to analyze information in patient records, assist doctors with diagnostics, and develop custom treatment plans based on the individual needs of each client. They can produce detailed diagnostic reports and provide recommendations based on the available data.
As AI technology grows more complex, new use cases are expected to be discovered.
Challenges with A2A Adoption
Even though A2A has significantly simplified multi-agent cooperation, it introduced new operational difficulties and security issues that are challenging to solve. The new standard was adopted across many industries. Companies were eager to implement it, hoping that the unified interface would help them make their products more powerful. However, after deploying such solutions, developers started to notice the following problems:
- Increased vulnerability. Hackers and other malicious individuals may target each assistant and a capability. Due to the wider attack surface, it becomes more difficult to protect the system against spoofing, prompt injection, or credential theft.
- Compliance issues. As tools within the system may exchange sensitive information, it might be challenging to ensure that each of them follows strict data protection guidelines.
- Latency. Longer agent-to-agent chains make it difficult to find the root cause of a specific issue, solve governance problems, and maintain observability.
Companies need to build and maintain increasingly complex infrastructure to avoid endpoint sprawl and issues caused by the changing structure of data sources. Solving these problems may require building an additional layer designed to enforce certain policies on A2A traffic. Such solutions can potentially safeguard tools from undesired exposure, protect sensitive information, prevent data leakage, and eliminate the possibility of schema drift.
A2A allows businesses to maintain the autonomy of each agent while focusing on collaboration. It involves the usage of widely adopted web technologies, including HTTP, JSON-RPC, and SSE, which simplifies its adoption. A2A is the best fit for asynchronous workflows, as it facilitates solving long-lasting issues. As the standard was developed with the help of leading industry companies, it’s expected that its deficiencies will be solved in the near future.
Final Thoughts
The Agent2Agent standard facilitates building autonomous AI systems with agents powered by LLMs. The protocol simplifies collaboration between various tools and services, increases interoperability, and efficiency. More organizations are expected to adopt it to automate their routines and optimize operations. MetaDialog builds advanced LLMs tailored to the needs of specific industries and enterprises. We specialize in AI technologies and develop advanced LLMs to help our clients simplify interactions with customers. Our custom AI models enable companies to automate up to 81% of replies to queries and optimize the routine of their customer support teams. Contact our managers today and discover how to harness the power of AI to better serve your customers.
