In the insurance industry, information is king. Data is vital to any insurance organization’s success: finding additional target audience segments to create effective advertising campaigns. However, as the volume of big data rises and the complication of the insurance field grows, standard analysis methods may not be enough, and there is a need to introduce non-standard artificial intelligence (AI) practices. It is where generative AI in insurance comes to the rescue.
By Market.Biz, the worldwide genAI market volume in the insurance field is expected to expand significantly; it is projected to grow from $346 million in 2022 to $5,543 million in the early 2030s. Let’s talk about how to apply generative AI in insurance.

Definition of GenAI
Generative artificial intelligence, also called genAI, is a modern modification of AI capable of writing, programming, analyzing insights, and performing various objectives based on current templates or teaching databases.
Unlike standard AI, with its reactive nature and collection of historical facts, genAI may learn and generate novel content. Such a technology is in the spotlight nowadays; genAI’s most famous platform is ChatGPT.
The effect of genAI is fantastic: in just a few months, ChatGPT has achieved 100 million active consumers, making it the fastest-growing program in the world. This high tech cannot be neglected; a last Celent survey found that 50% of insurers either examine LLMs or plan to do so in the coming months. Client service is seen as the most prospective area, but genAI could also refine underwriting and claims processing.
The Profits of GenAI in the Insurance Business
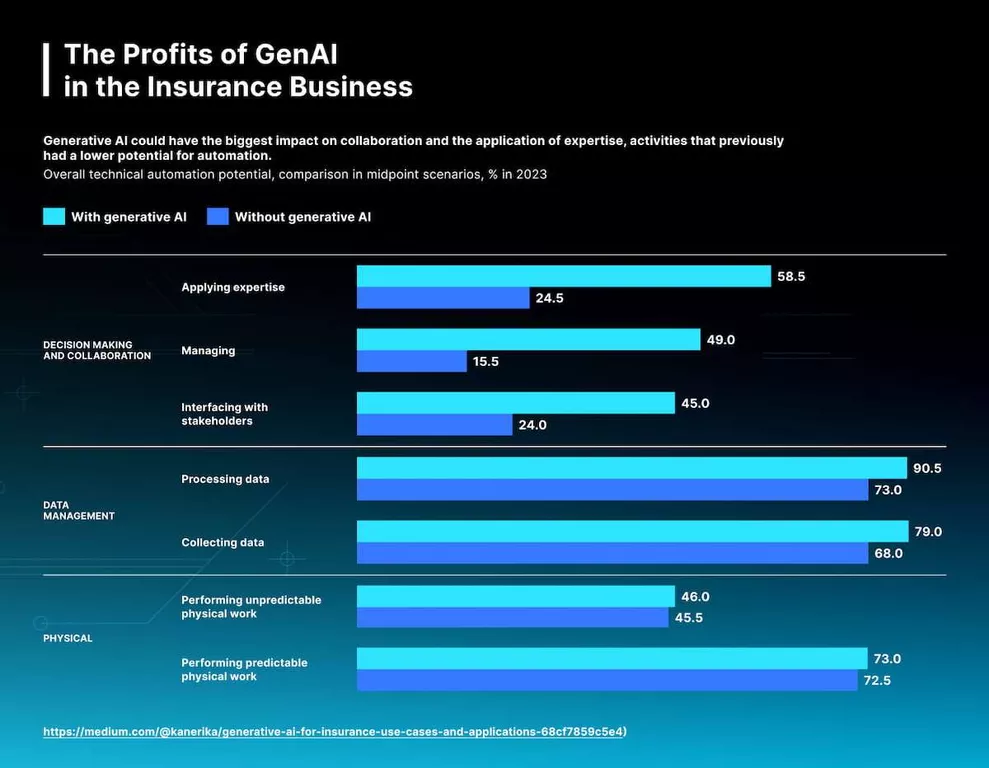
Boston Consultancy Group reports that AI-backed platforms provide significant efficiency and capital savings at every stage of indemnity pricing. One of the most important discoveries is the prospective savings of 40 to 60% in productivity and client service. It is estimated live agents today spend approximately 35% of their time researching conditions and policies. GenAI instruments allow you to reduce this time to fulfill fast and exact paper requests. Let’s consider other profits of such systems:
- Fraud detection capability: the insurance area faces a growing swindle problem, as evidenced by Coalition Against Insurance Fraud research. According to its evaluation, losses from insurance fraud in the United States reached $308 billion. GenAI suggests a solution to the problem: it models fraudulent and legitimate claims so that systems recognize potential scams.
- Faster AI claims processing: Ernst & Young LLP report data shows 87% of consumers report that their claims practice influences their loyalty to the firm. The implementation of genAI simplifies the claims management process. AI-backed solutions speed up claims settlement and decrease processing intervals by creating automatic responses to standard requests.
- Effective client collaborations: according to McKinsey research, genAI reduces human interactions by up to 50%. Its adoption in customer interaction may increase productivity, translating to a value raise of 30 to 45% of the current function costs.
While genAI allows insurers to be more systematic and offer new solutions, it is critical to remember that utilizing it requires an entire system, including interaction with live agents. It means the added value is generated only through a rational combination of AI-backed structures and live agent procedures and not just one AI platform.
Kinds of GenAI Structures in the Insurance
GenAI platforms enable the study and reproduction of templates and mechanisms present in the training database, letting them form samples similar to the initial dataset. In the aspect of AI-backed instruments in indemnity, the next groups of generative structures are distinguished:
- Generative adversarial networks (GANs) are groups of AI-ruled platforms that include multiple neural networks, a generator, and a discriminator taking part in a job. The generator builds fake databases, and the discriminator must distinguish between actual and counterfeit archives. In insurance, GANs are utilized to form fictitious but realistic libraries, e.g., demographic insights, requests, and estimates. Such patterns may complement existing learning data and raise the productivity of AI-backed solutions.
- Variational autoencoders (VAEs) mix modules of a generative structure and an inference system. VAE contains a few elements: decoder and encoder. The encoder modifies the initial insights into a latent environment representation, and the decoder restores insights from the latent environment back to the original conditions. Utilizing the sampling method from the explored latent space, VAE composes information with characteristic uncertainty, allowing you to obtain more diverse samples than when implementing GANs. It will enable you to create distinct risk opportunities to develop non-standard insurance products.
- Autoregressive structures are systems with a sequential data-forming procedure that forecasts each data dot based on the parameters of several past data dots. In indemnity, such instruments are utilized to form successive facts, e.g., time intervals about rewards, claims, and collaboration with contractors. The systems help insurers make forecasts, define deviations, and make rational decisions about business tactics.
The above structures create unique opportunities to compose novel data in the insurance. GANs allow you to form highly plausible templates, VAE suggests diverse and probabilistic facilities and autoregressive instruments let you manage consistent insights.
How to Utilize GenAI in Insurance?
The insurance value chain, from product creation to claims handling, is sophisticated. The ambiguous character of procedures such as risk evaluation and claims handling creates difficulties for the firm. GenAI is a prospective environment that optimizes processes and allows the introduction of individualized services. Let’s consider AI in insurance use cases.
Data growth
GenAI generates fictitious facts, which are helpful for firms that lack a particular category of archives for modeling. It raises the effectiveness of forecast structures.
Such synthetic databases repeat the properties of the original archives, but they lack personal insights, which allows you to maintain the anonymity of counterparties.
Content composing
AI in insurance area can be used to form content by applying different methods. Let’s discuss its most popular use cases in the organization’s activity:
- Policy documentation: AI may create policy papers relying on particular data. It automatically fills in some cells to speed up the document creation process.
- Marketing texts: AI can be utilized to generate personalized marketing materials, including brochures, blogs, social media posts, and email newsletters. It may compose content connected with various products personalized for distinct categories of clients.
- Collaborations with users: AI in customer communications for insurers may assist in creating emails, notifications, and messages for the target audience.
- Service descriptions: genAI can accurately describe a firm’s different insurance services. This data may be added to a webpage, brochures, or other promotional materials.
GenAI may quickly create large volumes of unique content for publication across multiple platforms.
Claims assessment
Claims handling is an essential activity in the insurance business. GenAI can be used to investigate and process claims efficiently. By examining the claim information and policy features, AI-backed techniques may define the response to the request, whether it should be approved, denied, or further investigated.
AI-backed structures can analyze the features of hundreds of claims filed under an insurance policy, which were accepted and rejected, and the reasons why it may produce specific results for future requests, following the same norms.
Virtual helpers and 24/7 support
Today, the relationship between insurers and clients is undergoing dramatic changes with AI-backed algorithms.
Modern chatbots and digital helpers can answer the most common questions and take part in sophisticated conversations. They can interpret complicated client requirements accurately, suggesting individualized policy advice and coverage data, enhancing user experience.
Automation of underwriting
GenAI refines the underwriting procedure by automating risk evaluation and decision-making. AI-backed platforms process historical archives, find templates, and evaluate risks, letting insurers make precise and effective decisions in AI underwriting. An insurance firm can adopt AI-ruled instruments to consider medical diagnoses, way of life, and genetic insights to make successful underwriting decisions, guaranteeing fast approval of policies and high quality of service.
Development of policies
GenAI can be utilized to form simple contracts. ChatGPT will quickly prepare a policy based on personal data about the client, including his age, medical history, and location. This personalization ensures more adequate insurance coverage to raise customer contentment.
Additionally, AI-backed platforms can identify market tendencies and adjust policies if conditions change or other insurers make corrections. GenAI instruments may provide notice to add a new clause that, e.g., excludes claims related to an epidemic or pandemic.
How to Build a GenAI Solution for Your Insurance Firm?
Preparing for the future in insurance demands firms to study the opportunities of genAI and strategically implement it into their procedures. Forming a generative AI environment involves performing several actions:
- Define your goals: be clear about the objectives you plan to achieve with genAI to ensure alignment with overall business tactics.
- Identify optimal use cases: evaluate the activities within your insurance firm where genAI can provide the most value, typically underwriting, claims processing, and client relations.
- Collect and analyze databases: collect actual and relevant data from various sources to successfully train genAI systems. Ensure confidentiality and information safety standards are met.
- Select an optimal variant: study the features of distinct structures and select systems that meet your use cases and firm requirements. Keep in mind factors such as scalability, interpretability, and implementation complexity.
- Model teaching and customization: you may train AI-backed structures on high-quality databases and fine-tune them with iterative feedback loops. Regularly monitor and update mechanisms to ensure maximum performance.
Now, you can add AI-backed structures to your insurance systems and analyze their effectiveness. Monitor critical parameters, evaluate the impact, and make the necessary changes to maximize benefits.
The Main Challenges with GenAI
Like many disruptive technologies, AI in insurance offers robust solutions to some problems and introduces challenges. It is essential to analyze these troubles before adopting such an instrument into your enterprise to transform your business successfully:
- Accuracy: Although AI-backed platforms are taught on large volumes of data, they are machine learning (ML) platforms and may produce false data. Reviewing all content generated by your AI-backed instrument before using it is critical.
- Information confidentiality: customers must control the information they collect and transmit through AI-backed structures. Although firms take measures to guarantee cybersecurity and the protection of client information, confidentiality and data protection risks remain.
- Bias: genAI systems may unintentionally learn biases in the databases they were educated on. Biased records can lead to unjust pricing, discrimination against specific demographic groups, or even incorrect claims decisions. Insurers must responsibly select and process learning data to ensure fair results.
Don’t forget about the ethical component. A study published in Insurance Business Mag cites a survey to suggest clients weren’t too excited to encounter ChatGPT in their interaction with insurance organizations. According to this study, approximately three in five users (59%) say they have little or no trust in genAI. Although such techniques may refine client service, about 70% of respondents prefer collaborating with live agents.
Which Famous Insurance Firms Are Introducing GenAI?
Active application of genAI by large insurance organizations can change the area, raise operational efficiency, and refine decision-making procedures and the quality of cooperation with clients. Let’s consider the primary members of the insurance market that have achieved success in the introduction of AI-backed instruments:
- Lemonade (New York) uses AI-backed platforms and behavioral factors to provide property owners and renters insurance. The firm utilizes artificial intelligence in underwriting and requests processing to guarantee fast and straightforward indemnity coverage. Lemonade is investing in genAI to automate a large number of business procedures.
- Liberty Mutual (Boston) is a multidisciplinary worldwide organization that suggests a long checklist of insurance products and services. Incorporating ideas from Solaria Labs, Liberty Mutual is experimenting with AI and ML, e.g., implementing an AI-backed vehicle damage calculation system that quickly assesses automobile damage.
- Clearcover (Chicago) is a well-known operator of digital auto insurance services that uses modern techniques to select the lowest possible prices and optimize client practice. ClearAI’s artificial intelligence solution provides insurance automation in claims processing, guaranteeing fast and exact responses.
Adopting insurance artificial intelligence in these firms will provide many profits, including personalized offers, claims processing, fair risk assessment, and growing client contentment. However, they should not forget about the safety of insights, compliance with norms, and human control.
Final Words
GenAI is modifying the insurance area today by raising operational productivity, creating new capabilities, and deepening client relationships. Insurers must act consciously and have modern instruments to minimize the risks connected with these techniques.
MetaDialog is at the vanguard of reorganizing insurance by introducing next-generation AI-backed platforms. Leveraging the opportunities of cutting-edge technologies, we strive to redefine how insurance procedures are conducted, providing users with the most efficient, precise, and customer-centric apps.
Our non-standard application of GenAI automates and optimizes various sides of indemnity procedures, ensuring users obtain optimal services. You can now book a demo to get your LLMs and Conversational AI based on your dataset.
